



Applications | SOPTOP SZX12 research-grade stereomicroscope assists in the description of a new species of Chinese Indo-Chinese stream crab, Ctenopharyngodon idellus.
Release time:Release time:2024 - 01 - 15
China has the highest species diversity of freshwater crabs in the world, however, many new taxonomic units remain to be discovered.
The Sino-Indian stream crab genus Indochinamon Yeo & Ng, 2007 is characterized by high species diversity, with 41 species recorded, and it mainly inhabits mountain streams in southern China, northern Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, Myanmar and northeastern India.
Prof. Sun Hongying's team from the School of Life Sciences, Nanjing Normal University (NNU) discovered and described a new species of the genus, Indochinamon frontatum, during field surveys in Yunnan Province, China, which is morphologically distinct from other closely related species.

SOPTOP SZX12 is a research-grade parallel-optical path continuous-division body-viewing microscope with superior Galilean optics and excellent imaging performance, which can meet the needs of biological experiments, chemical analysis, cell culture and other research needs.
The research team observed the specimens through the SZX12 and took microscopic images with the OD500F camera (Figure 1). Such collection was found to have the following morphological features: cephalothoracic armor nearly trapezoidal (width to length ratio of 1.4), dorsal surface slightly convex, sparsely setose, H-shaped grooves obvious, and gill area with oblique striations; frontal area wide and with obvious crests Posterior frontal ridge is obvious and not connected with the posterior ocular ridge; Posterior ocular ridge is obvious. External eye socket angle bluntly triangular; anterior gill teeth serrated; posterior lateral margin almost straight (Fig. 1A).

▲Fig. 1 Male orthotype specimen of the frontal ridge mid-Indian stream crab, NNU16-7472-01: (A) dorsal view; frontal view (B); ventral view (C). Scale bar: 10 mm.
The SZX12 adopts a 22mm large field of view eyepiece, which allows the research team to obtain a wider image, and even the edges are brightly and clearly displayed: the third maxilliped sitting segment of the specimen is rectangular in shape, with a smooth surface and a distinct median line, and the long segments are sub-square, and the end of the exopod extends about 1/3 of the way to the base of the long segments, and is whippeted (Figs. 1B, 2A)
Both chelicerae slightly asymmetric, dorsal surface of carpal segment finely rugose, inner terminal angle with sharp spines, its base with a small spine; length of palp of chelicerae ca. 1.7 times height, ca. 1.3 times length of movable finger, inner margins of both fingers with obtuse teeth, few gaps when closed. Pedipalps flattened and stout, length of anterior segment of last pair of pedipalps about 1.7 times width, about as long as phalanges (Figs. 2B-D).
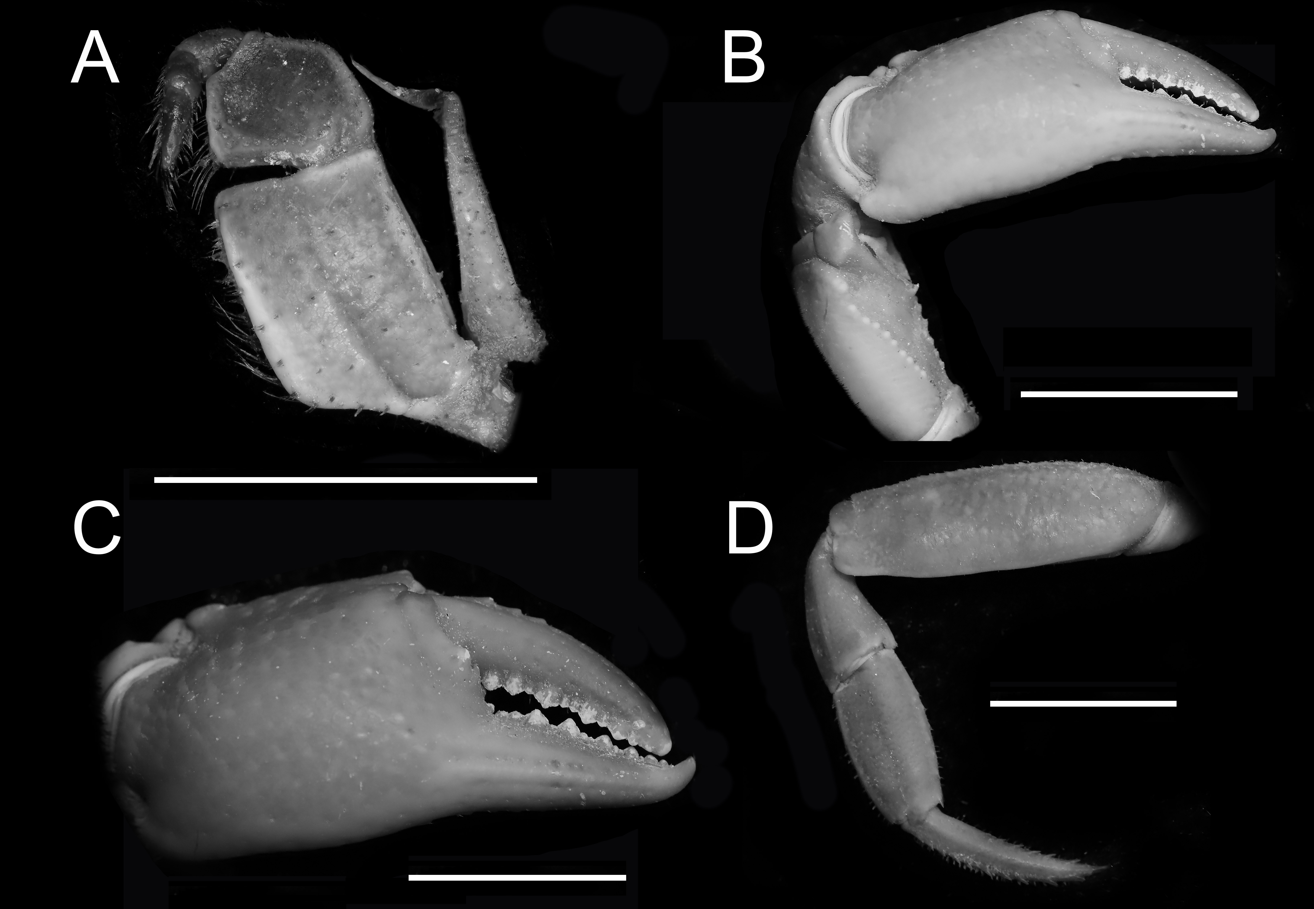
▲Fig. 2. Male orthotype of the frontal ridge mid-Indian stream crab: left third jawed foot (A); large chela (B, C); two-step foot (D). Scale bar: 10 mm.。
Through the reflector adjustment device on the base of the SZX12, the light illumination range can be changed to obtain images with different effects. The research team found that the specimen's thoracic armor is smooth, with hemp concave points; the first and second thoracic segments are completely healed in a triangular shape; the second and third thoracic seams are obvious and complete; the third and fourth thoracic seams are inconspicuous, with only shallow grooves on both sides; and the thoracic ventral armor grooves are beyond the midpoint of the basal segments of the chelicerae. Male abdomen triangular, caudal segment narrowly triangular, terminal margin bluntly rounded. Female abdomen broadly rounded, caudal segment semicircular. Reproductive pores situated on fifth and sixth thoracic carapace sutures, oval, covered (Fig. 3).
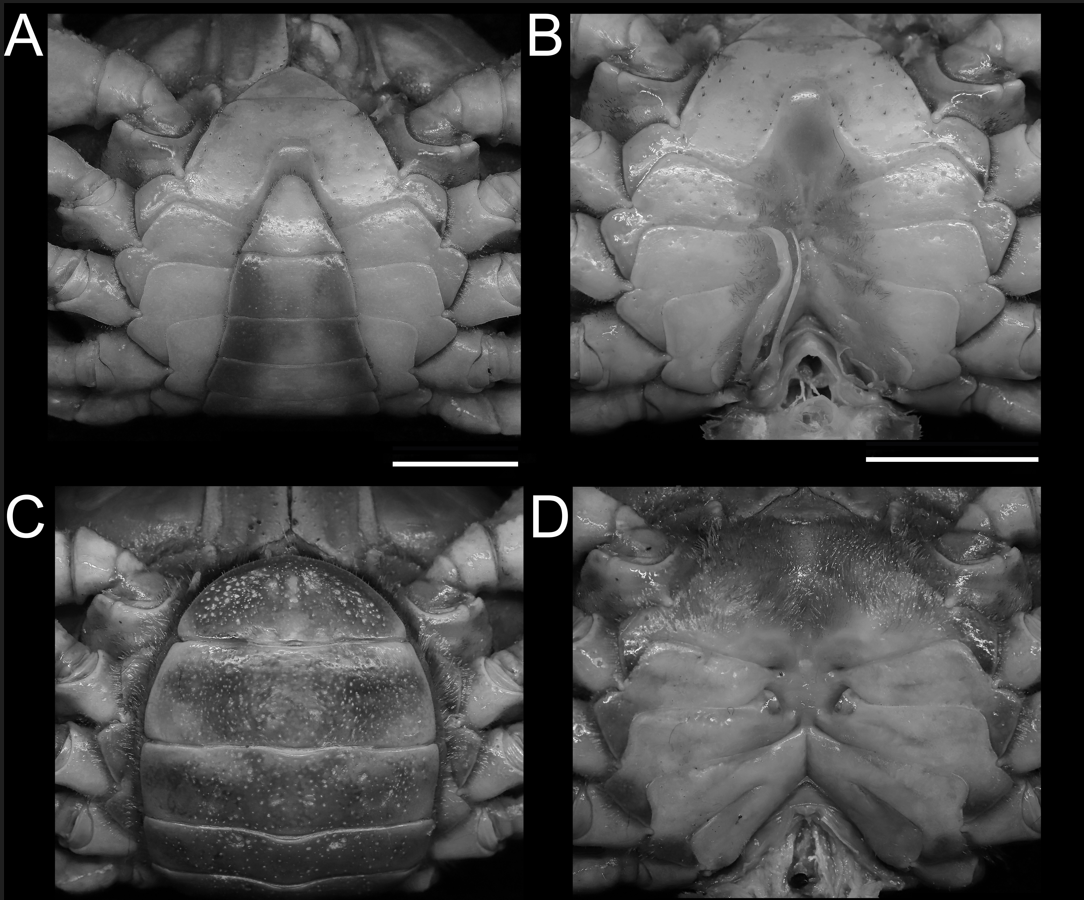
▲Fig. 3. Frontal ridges of mid-Indian stream crab male orthotype (A, B); female paratype (C, D); thoracic ventral armor (A, C); G1 in natural position (B); female thoracic armor and genital pore (D).。
G1 elongate, distinctly curved, terminal segment hooked, curved outward by about 45°, dorsal lobe extending along proximal one-third to one-half of terminal segment; proximal segment of last two segments broad, with cervical distal end; G2 elongate, longer than G1 (Fig. 4)。
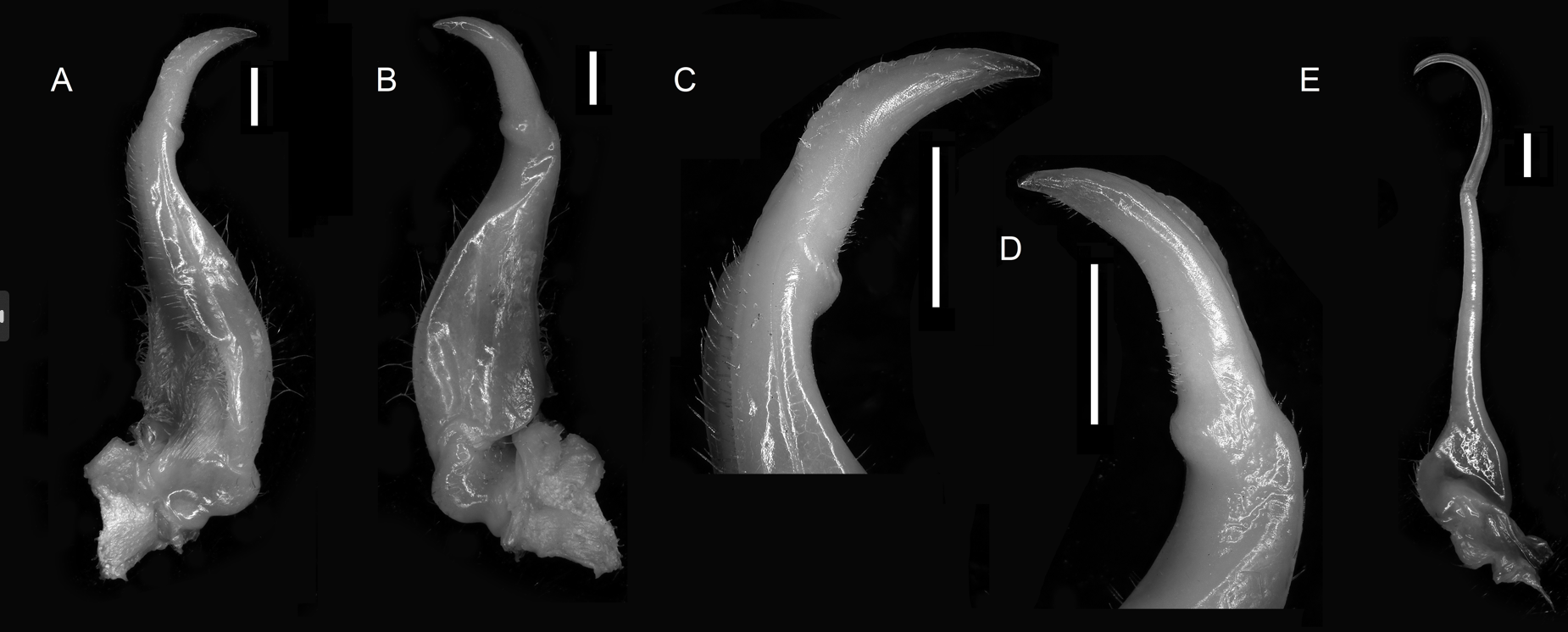
▲Fig. 4 Male orthotype specimens of the frontal ridge mid-Indian stream crab: left G1 in ventral view (A) and dorsal view (B); left G1 terminal segment enlarged in ventral view (C) and dorsal view (D); left G2 (E). Scale bar: 1mm
Original link:Shi BY, Pan D, Sun HY. 2023. On a new species of freshwater crab from southern China (Crustacea, Brachyura, Potamidae). Zootaxa. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5383.4.8
Return list
