



Scientific Innovation | IRX60 facilitates new breakthroughs in disc nucleus pulposus regeneration therapy!
Release time:Release time:2024 - 06 - 19
Low back pain is one of the most common disabling disorders worldwide, affecting approximately 568 million people worldwide.
Low back pain is closely associated with intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD), which causes loss of water and proteoglycans from the nucleus pulposus (NP) of the intervertebral disc, as well as disturbances in the extracellular matrix.
Currently, patients with IVDD usually receive conservative treatment or surgery, but none of these methods can truly restore the structure and function of the intervertebral disc and may even lead to side effects. Therefore, there is an urgent need to find therapeutic strategies that target the causes of IVDD.
Renhe Hospital of Three Gorges University published a paper titled “Nanofber reinforced alginate hydrogel for leak-proof delivery and higher stress loading in nucleus pulposus” in Carbohydrate Polymers (CAS Region I Top Journal, IF=11.2). The research result entitled “Nanofiber reinforced alginate hydrogel for leak-proof delivery and higher stress loading in nucleus pulposus” was published in the Journal of Carbohydrate Polymers (IF=11.2), in which a nanofiber reinforced injectable hydrogel was prepared, which not only provides mechanical support to help repair the nucleus pulposus, but also promotes the reconstruction of the tissue environment, and ultimately realizes the regeneration of nucleus pulposus.

The research team designed core-shell structured nanofibers (NF-SF/PRP) as the main carrier for loading platelet-rich plasma, prepared the nanofibers by coaxial electrostatic spinning, and homogeneously mixed the formed nanofibrous membranes into the sodium alginate hydrogel precursor solution. Finally, calcium chloride was injected with a syringe to form the hydrogel.
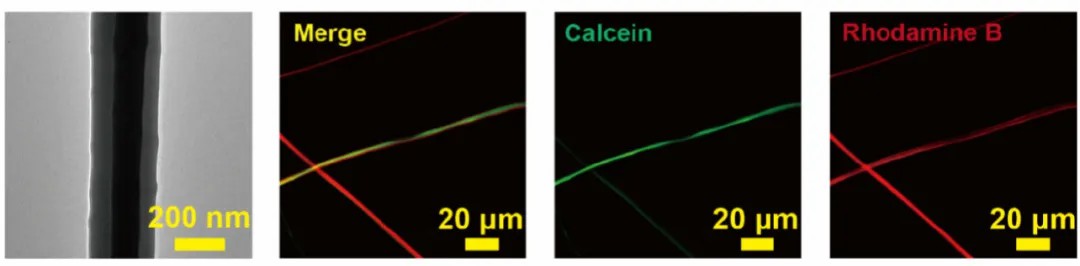
The researchers observed the core-shell structure of NF-SF/PRP by SOPTOP IRX60 research-grade inverted fluorescence microscope.

As shown below, the core-shell nanofibers exhibit two different colors, platelet-rich plasma with green fluorescence is located in the core of the nanofibers, and filamentous nanofibers with red fluorescence are distributed on the surface of the nanofibers around the PRP. These images show that platelet-rich plasma was successfully bound and uniformly distributed within the nanofiber core.
In addition, the researchers further investigated the biological and drug-carrying properties of the hydrogel in vitro and showed that the hydrogel had negligible toxicity to human fibroblasts by live/dead cell staining.
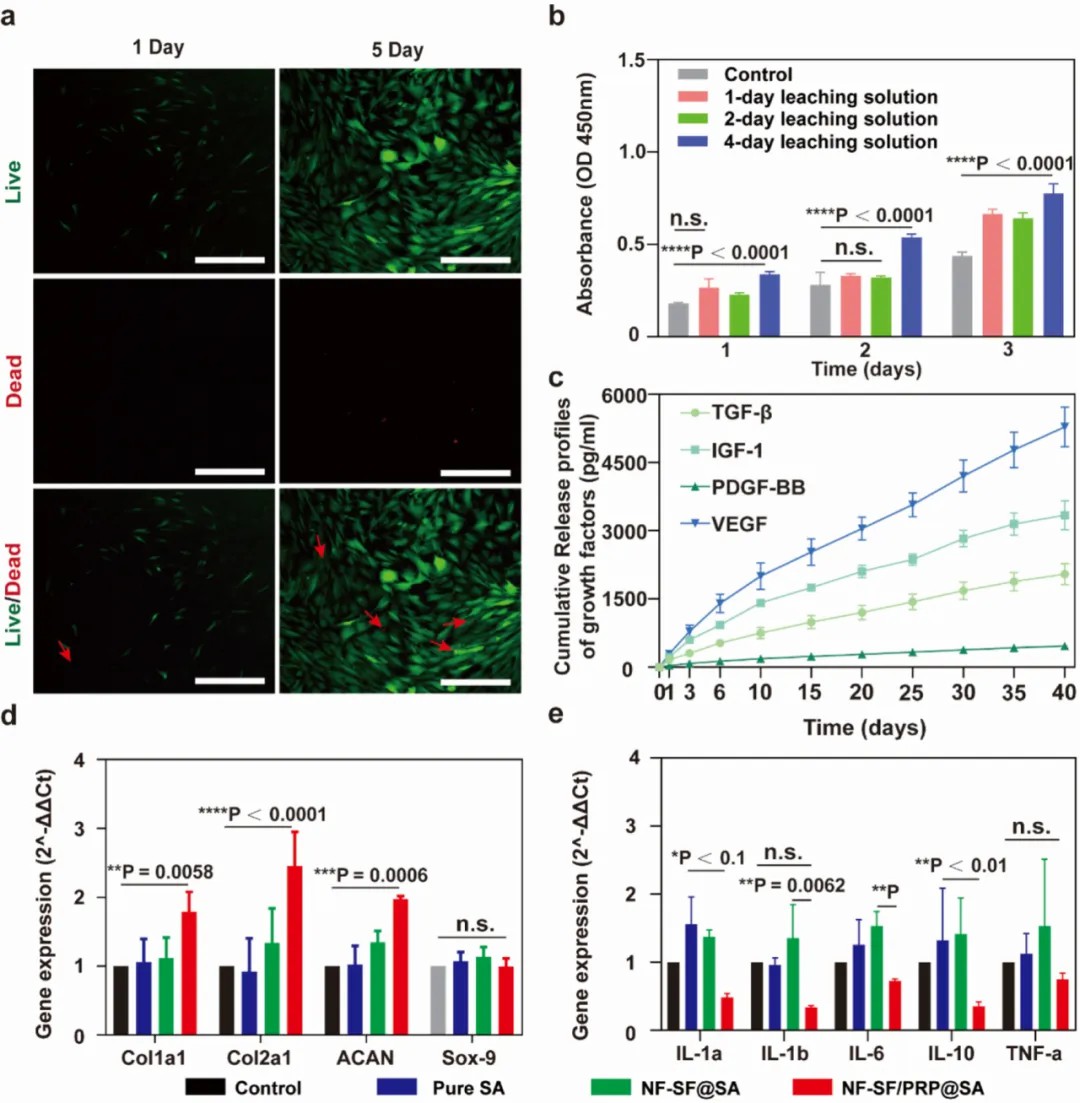
In this study, we demonstrated that nanofiber-reinforced injectable hydrogel can effectively deliver platelet-rich plasma, prevent it from leaking, and enhance the mechanical strength of the hydrogel to help repair the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral discs, which provides an effective and regenerative therapeutic viable option for enhancing biomechanics and restoring intervertebral disc function.
Paper Information:Li M, Wu Y, Li H, Tan C, Ma S, Gong J, Dong L, Huang W, Li X, Deng H. Nanofiber reinforced alginate hydrogel for leak-proof delivery and higher stress loading in nucleus pulposus. Carbohydr Polym. 2023 Jan 1;299:120193.
doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120193. Epub 2022 Oct 7. PMID: 36876807.
Return list
