



Scientific Innovation | Resveratrol improves maternal immune activation (MIA)-induced autistic ASD-like behavior in mice
Release time:Release time:2024 - 05 - 24
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that occurs primarily in children and is characterized by social dysfunction and restricted, repetitive behaviors or interests.
Maternal infection during pregnancy is an important cause of ASD in the offspring, and inflammatory infiltrates caused by maternal immune activation (MIA) can lead to fetal neurodevelopmental disorders.

According to epidemiologic surveys, approximately 78 million people worldwide suffer from ASD, and the number of people with ASD has increased rapidly over the past 20 years.
However, some of the drugs used to treat ASD have limited effectiveness and cause side effects such as hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and weight gain. Therefore, there is an urgent need to find more effective treatments.
Recently, the Department of Pediatric Health and Maternal and Child Health, School of Public Health, Harbin Medical University, published a paper entitled “Resveratrol regulates Thoc5 to improve maternal immune activation-induced autism” in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry. Resveratrol regulates Thoc5 to improve maternal immune activation-induced autism-like behaviors in adult mouse offspring” (First author: Zeng Xin, Fan Linlin; Corresponding author: Wu Lijie, Liang Shuang). Based on the concept of homology of traditional Chinese medicine and food, we verified the effects of resveratrol on maternal immune activation-induced ASD-like behaviors in mice. ASD-like behavior in mice induced by maternal immune activation.

Using an integrated bioinformatics approach, the research team conducted a large-scale screening and analysis of medicinal herbs and drug targets, and identified resveratrol and Thoc5 as the best small molecule components and drug targets, respectively, for the treatment of ASD-like behaviors induced by maternal immune activation in mice, which were found to be able to increase the expression of Thoc5, as demonstrated by the results of in vitro experiments.
To better validate the medicinal potential of resveratrol, the researchers conducted in vivo experiments on mice and observed the expression of Iba-1 (a marker of microglia) in the fetal mouse brain by SOPTOP laser confocal scanning microscop.
The expression level of Iba-1 in the brain of MIA fetal rats was significantly higher than that in the PBS group, but after pretreatment with resveratrol, the expression of Iba-1 in the fetal brain was significantly reduced.
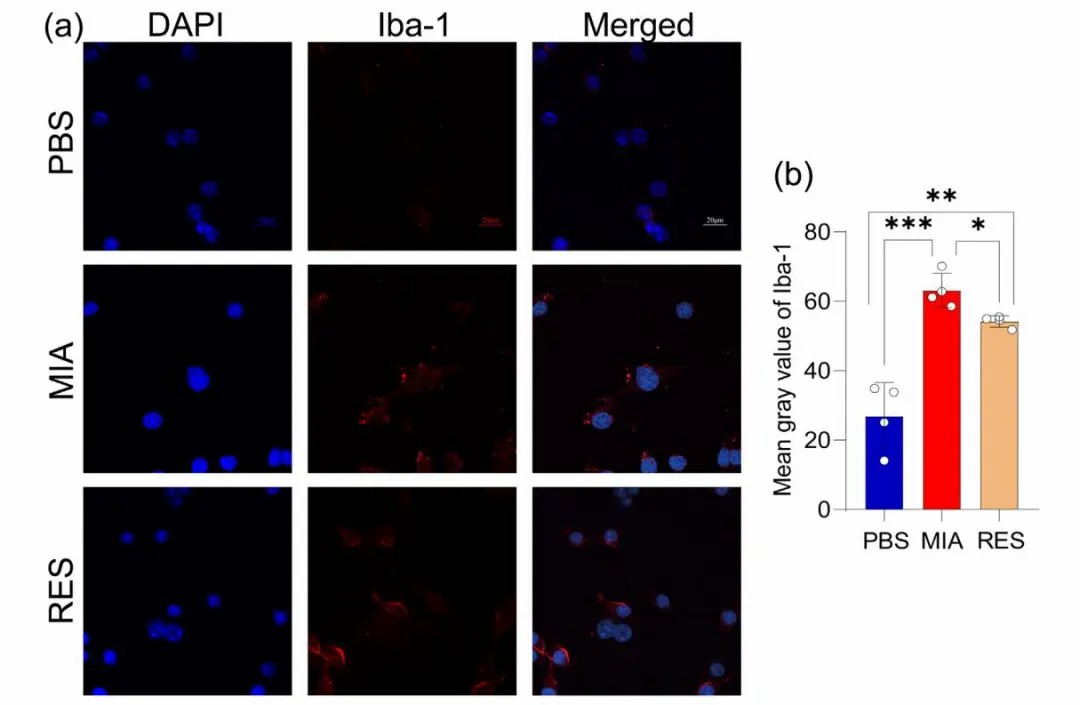
▲Observation of Iba-1 expression by immunofluorescence method
This study is the first comprehensive exploration of the active ingredients and targets of medicinal herbs for the treatment of ASD. Through in vitro and in vivo experiments, it was successfully demonstrated that resveratrol can increase the expression of Thoc5, decrease the level of IL-6, and inhibit MIA-induced inflammation of the placenta, fetal brain, and cerebral cortex of the offspring, and improve ASD-like behaviors in adult offspring.
Thesis Information
Zeng X, Fan L, Li M, Qin Q, Pang X, Shi S, Zheng D, Jiang Y, Wang H, Wu L, Liang S. Resveratrol regulates Thoc5 to improve maternal immune activation-induced autism-like behaviors in adult mouse offspring. J Nutr Biochem. 2024 Apr 5:109638.
doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2024.109638. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38583499.
Return list
